While the controversy over the integrity of elections in free software communities is significant, a far more serious issue for all communities right now is the spectre of secret punishments and other practices that involve shaming people. Debian has recently experimented with these reckless practices and it would be wise to ensure they are not repeated or replicated in any other community.
Secret punishments exploit shame to maintain secrecy and avoid controversy. For example, many pedophiles know they can keep offending because shame will keep their victims from talking. There is a close connection between the use of secret punishments and the pursuit of political objectives, for example, isolation of asylum seekers, which is now classified as a form of torture. People in positions of authority see shame as an opportunity to indulge themselves in occasional acts of bullying, hoping their conduct will never be subject to scrutiny and maintaining their otherwise immaculate reputations.
This reveals an interesting feature of shame: people feel shame whether they did something wrong or not. An innocent thirteen-year-old victim of a pedophile feels shame. A rogue trader who knows he is guilty feels shame too. It is the same emotion for somebody guilty or somebody innocent.
Consider the statistic that on average, it takes 30 years for a victim of child abuse to come forward. Shame is the poison that prevents them from talking. Yet some victims of this abuse do choose to come forward.
In the Debian crisis, different people waited different periods of time before they could talk publicly about the way they were used in unethical experiments. One reason for this is that nobody wants to hurt the Debian Project, everybody had made efforts to communicate with the so-called leaders privately many times before it became a public issue. But if we ignore those attempts at private communication, there is also a probability that shame was a factor in remaining silent, not telling anybody else, even though the punishments were either completely inappropriate or way out of proportion to any mistakes.
Some people may feel it is a little indulgent linking child sex abuse to online abuse. It turns out, research published in Social Psychology of Education found that psychological impacts of online bullying, which includes shaming, are just as harmful as those from child abuse.
When operating in an online community, such as a free software organization, we tend to know very little about each other and our wider circumstances. People rarely disclose details of personal tragedy, physical and mental illnesses, pressures in their home or work environment or anything else of an emotional nature. To give one example, well known in the HR world: thirty percent of people will experience a depression at some point during their life. In a community of 1,000 people like Debian, it is almost a certainty that every year, some are going to experience a major depressive episode. In fact, for people aged 18-25, it is close to 1 in 10 people.
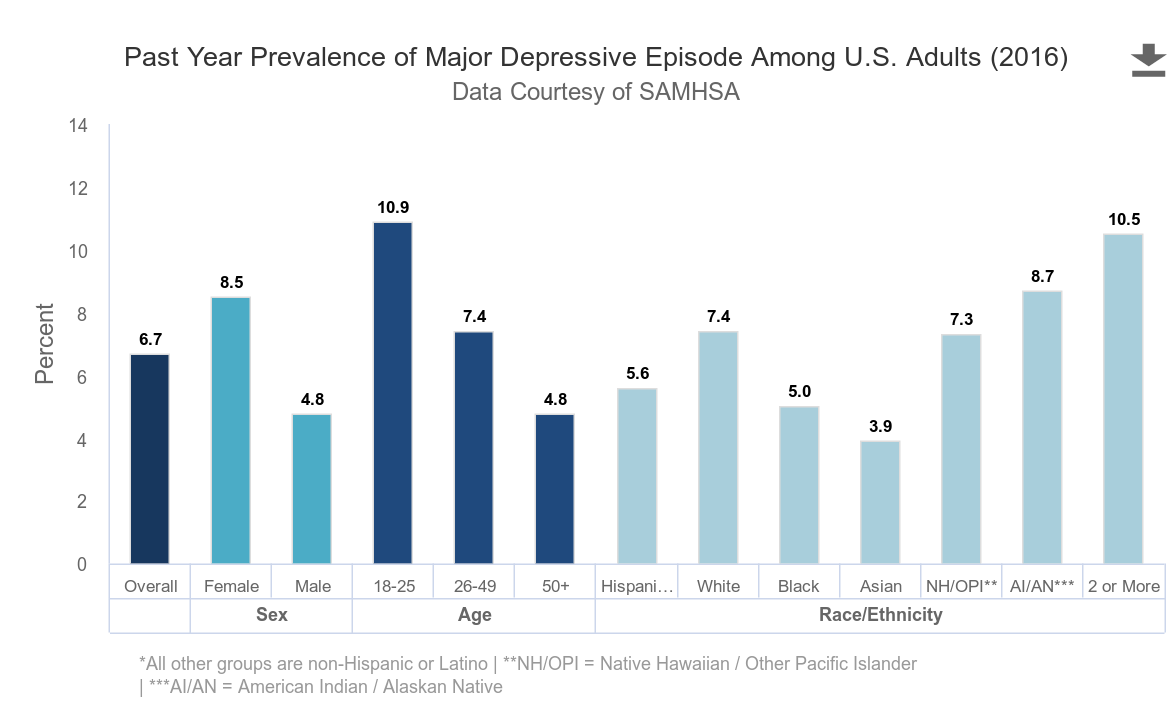
If you are a leader in an online community and you decide to use secret punishments as a tool, if you inflict some kind of shame on ten people each year, what is the chance that one of them might already be unwell and your actions cause them further harm?
In one of the more extraordinary cases, the father of a thirteen year old girl cut off her hair as a punishment. The punishment/shaming was recorded on a video and uploaded online.
A few days later, she jumped off a bridge.
It is scary to contemplate how many other members of the free software community may have received a heavy-handed email from the leaders or "anti harassment" teams that may have made them feel shame. Many people have been reading blogs about the challenges community representatives faced in free software organizations. People have confided privately about additional incidents, intimidating emails from project leaders, that were not disclosed publicly. Yet there may be even more victims who have not spoken to anybody, or somebody who is tying themselves in knots, unsure how to start a conversation about their "anti harassment" experience.
In the well known management book One Minute Manager, it is suggested that leaders give people one minute reprimands, finishing with some sort of praise. The type of reprimands and threats people have received from "anti harassment" and "safety" teams have no resemblance to that, they often contain big lists of perceived failings. They CC a whole bunch of people to add extra humiliation and shame. Rather than finishing with praise, they finish with a threat or punishment, to sustain the shame. There are many examples of Chris Lamb behaving this way.
Thinking about it another way, shame is like fat or salt. Small quantities of fat and salt are important in our diets but excessive quantities cause harm. Small quantities of shame may deter us from bad behaviour. Large amounts of shame are more likely to do more harm than good.
Reflect on the vast difference between our online communities and real-world environments. In the real world, an employee might simply get a doctor's note and stay away from the office during a period of illness. Their employer could not accidentally punish them because they are not present in the office. In the online world, there are no doctor's notes. Once again, 16 million American's reported suffering depression in one year but how many would have put their email account in vacation mode with an auto-response about their condition?
In the online world, it is a lot easier to hide that stuff, so people do.
Another striking feature of the Debian scandal is that no due process was followed, even though at least one person had earlier asserted they were dealing with an extraordinary situation in their private life, the leaders made not the slightest attempt to start two-way communications. This rude and reckless attitude demonstrates utter contempt for the welfare of the people they interact with.
Making punishments like this becomes a game of Russian Roulette: most of the time no harm is observed but every now and then, it goes badly wrong, like the girl who jumped off a bridge. It is a reckless game indeed. No free software community would want to be associated with an incident like that.
Responsible online communities need to denounce the use of punishments and shame, just as most responsible countries have denounced the use of land mines and biological weapons.
Personally, as we continue to observe the way certain leaders take a flippant and callous attitude to these issues, it leaves us feeling that it is better not to remain associated with those figures until the welfare of all community members becomes a priority. Hundreds of fellows already decided to cut all ties with FSFE, none have had any regrets about that.


